- About K-water Institute
- Technical Support
- International Cooperation
- Press Center
About K-water Institute
K-water Satellite Field
Vision
Provision of total solution to improve healthiness of tap water
Main business
Securement of trust in tap water adjusted to customers' need
- - Encouraging to drink tap water by constructing clean tap water environment healthy to human body
- - Making continuous efforts to secure safety in water quality by investigating 250 items of the entire process of drinking water
Reinforcement of global competitiveness by developing analytical methods and strengthening the role of official institutions
- - Leading global analytical competitiveness by developing high-level cutting edge analytical methods
- - Securing international public confidence by expanding global workmanship comparison test
Prompt solution of problems with active support to environmental issue
- - Fast solution and aggressive response to environmental issues such as water quality, soil, and ecosystem
Operational direction
Provision of total solution to improve healthiness of tap water
Construction of new foundation
for tap water
- Researching the healthiness of tap water for the nation in order to realize water welfare
- Developing future techniques adjusted to customers' need
Prompt support to current
issues on field
- Promptly solving current issues with diversified analysis
- Giving customized support responsibly through work circulation
Maximization of
analytical capability
- Strengthening global analytical capability by developing cutting- edge analytical Methods
- Strengthening the role of official institutions and invigorating the network
About the department
Water Quality Research Center, as an institute specialized for water analysis, takes the initiative in establishing highly reliable water quality analytic system and providing healthy tap water to the nation by securing world-class facilities and analytic capability. The center is composed of experts in various major fields such as water quality, soil, ecology, chemistry, and biotechnology.
Inspection of 250 items on tap water
Water Quality Research Center inspects 250 items on raw and tap water in metropolitan and local water service operated by K-Water for the purpose of providing safe and healthy tap water.
Introduction of "self-inspection items" for the first time among water service providers in Korea
Construction of pool on 500 items of water analysis and development and application of real-time quick analytic
methods such as multi-item simultaneous analytic technique and micropollutant screening analytic technique Securement of safety in drinking water and verification of tap water quality by performing inspection on 250 items, which is more strengthened than that of the advanced countries, e.g. USEPA (110 items), WHO (173 items), and Japan (121 items).
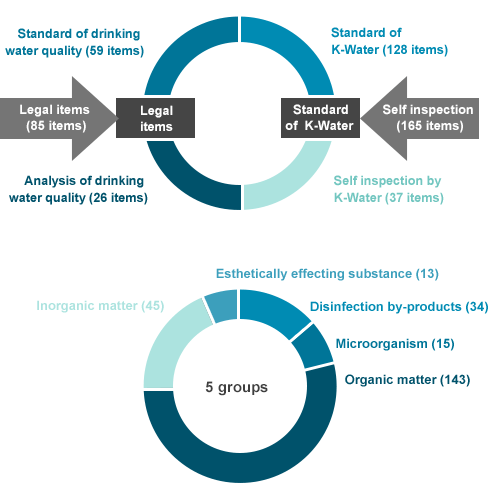
- Legal items(85 items)
- Standard of drinking water quality(59 items)
- Analysis of drinking water quality(26 items)
- Self inspection(165 items)
- Standard of K-Water (128 items)
- Self inspection by K-Water(37 items)
- 5 Groups
- Organic matter(143)
- Inorganic matter(45)
- Disinfection by-products(34)
- Esthetically effecting substance(13)
- Microorganism(15)
Current state of the composition of 250 items
- - 85 legal items (59 items of drinking water quality standard and 26 items of drinking water quality observation
- - 165 items of self-inspection by K-Water (128 items of self standard and 37 items of self observation)
- - Divided into 5 groups of disinfection by-products, microorganism, organic matter, inorganic matter, and esthetically effecting substance
Result of performing such inspection from 2002 to 2013
- - No detection of organic matter with noxious effect such as phycotoxin, microorganism, plasticizer, and alkyl phenol
- - Ion and inorganic metals: Detected in low concentration compared to the drinking water quality standard or the self-standard of K-Water
- - Disinfection by-products: Detected in low concentration compared to the drinking water quality standard or the self-standard of K-Water
- - Agricultural pesticides and perfluorine compound: Detected in extremely low amount compared to the guideline of
USEPA and WHO for drinking water
→ Having the safeness of tap water from micropollutants verified
Operation of authorized institute
In a bid to produce reliable data, it operates 9 authorized institutes in Korea and abroad, designating the first international test agency among the current waterworks business operators and the only international workmanship test agency in Korea.
Securing public confidence and dominating Korean and overseas analytical areas with 9 designated and authorized official institutes
Securing public confidence by operating official institutes and capable to issue official report to over 69 countries
Securing global competitiveness in water analysis area and improving brand value as a certification institute with the best analysis capability
Main performance
- - Being selected as an excellent international test institute in 2008 (Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy)
- - Performing global workmanship test on water quality for the first time in Korea in 2012 (evaluation of analysis accuracy of
international certification institutes) - → Having 51 overseas organizations from 51 countries including USA and Japan as well as 82 Korean organizations including
Seoul participated for 3 years (2012 to 2014) - - Being selected as the best international test institute in 2013 (Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy)
| Contents | Date |
|---|---|
| International test institute (KOLAS) | May 6 2003 (first among water service providers) |
| International workmanship test institute | November 30 2009 (only institute among water service providers) |
| Drinking water quality test institute | November 18 1998 (first in Gum river Area) |
| Soil-related special institute (soil contamination investigation) | October 21 2002 |
| Agency for testing the accuracy of environmental measurement equipment | April 4 2006 |
| National reference standard data center | January 8 2014 (first in environmental area in Korea) |
| Virus test institute | March 19 2003 (first in Korea) |
| Institute for investigating Norovirus of underground water | June 19 2009 (first in Korea) |
| Protozoan test institute | September 15 2004 |
Technical support to environmental issues
Total 279 technical supports and tangible effects worth 43.28 million won from 2006 to 2014
24-hour quick response to abnormality in water quality and new environmental issue with analysis techniques and capabilities of Water Quality Research Center
- - Analysis on phenol and formaldehyde related to phenol spill at Nakdong River (2008)
- - Investigation of the actual condition of melamine incident related to melamine contamination in dairy products from China (2008)
- - Investigation of the actual condition of Tamiflu incident according to the prevalence of new influenza (2010)
- - Investigation of the actual condition of radioactive substance related to radioactivity leakage from nuclear facility in Fukushima, Japan (2011)



Water sommelier
Introduction of water sommelier training course in 2011 for the first time in Korea and registration of private certificate for the purpose of making positive 'healthy and delicious' image on tap water and encouraging the nation to drink tap water
※ Having produced 112 water sommeliers as of 2014
Securing dominant position in tap water quality management and strengthening the professionalism of water service institute, responding to a change in paradigm of tap water from safe water to delicious one



Key techniques
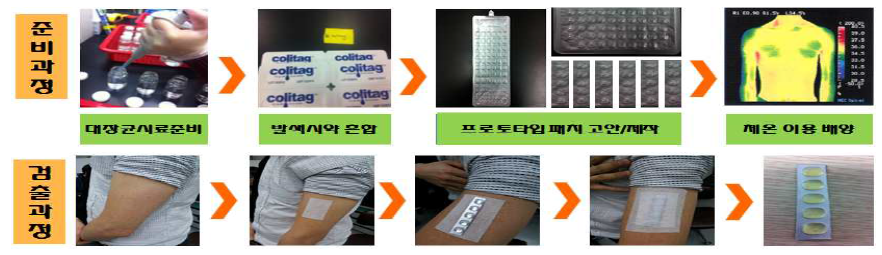
Method of detecting Total coliform bacteria using body temperature
Appropriate technology for testing Total coliform bacteria with the use of body surface temperature instead of incubator requiring electricity
* Patent applied (October 15, 2013, Application no. 10-2013-0122445)
Algae-controlling agent nontoxic to plants
Technique that can effectively remove green algae, which is the main cause of bad taste and smell, without causing secondary pollution or phxtotoxicity
- * Patent applied (March 5 2014, Application no. 10-1373399)
- * Designated as a new technology (Korean Environmental Industry & Technology Institute), registered as water-treatment
agent (National Institute of Environmental Research), registered as algae remover in Ministry of Environment
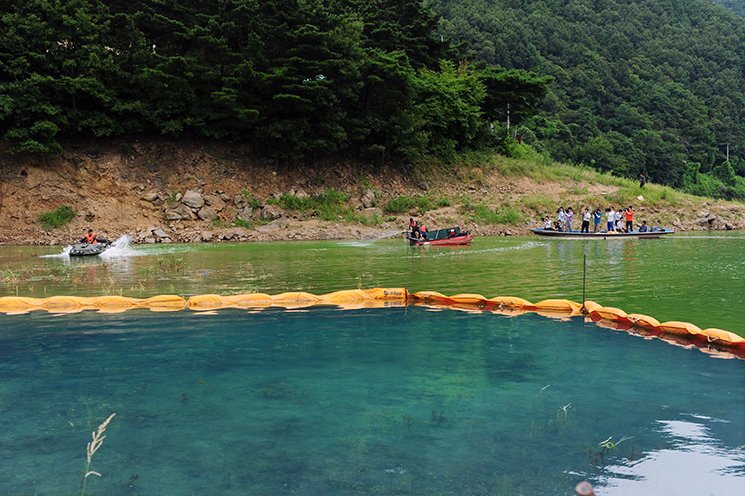

Actual scene of algae removal
Research tasks
Securement of high-value key technologies and solution of current issues through research and development
Details of business progressed and performance
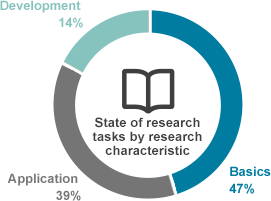
- - Performing 110 company's and consigned research tasks from 2002 to 2014 For research characteristic, basic research has been conducted the most.
47%: Basic research areas including the establishment of analysis techniques
39%: Application research areas including water analysis during supply process
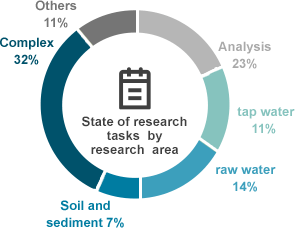
14%: Development research areas including the development of various analytical machines and analysis methods - - For research area, complex research (establishment of analysis methods+tap water, raw water+tap water)
has been conducted the most.
Current main research tasks
- - Research for optimizing method of analyzing underwater dioxins (2004 ~ 2005)
- - Quick detection of water-borne virus with the application of real-time gene analysis method (2005 ~ 2007)
- - Research on standardization of multi-item simultaneous analysis method with the application of mass analysis (2007 ~ 2009)
- - Research on preventive water quality management with the use of screening analysis technology with high resolving power (2010 ~ 2011)
- - Research on water-borne microorganism pollution investigation technique for securing safety in drinking water (2013 ~)
- - Research on the effects of tap water on the nation's health (2014 ~)