management Response to
harmful algal blooms Supply of
healthy water Expansion of
water welfare Integration of water infor
mation based on Big Data
Integration of water information based on Big Data
- About Big Data
-
Big Data indicates massive data that cannot be collected, saved, searched, or analyzed in previous ways owing to greatness in data quantity (size), format and input/output speed with those of the existing data.
Digital data produced worldwide in 2013 is reported to be 1.2 trillion GB. With such geometric increase in data quantity, interest in the project of Big Data that analyzes new values extracted from mass data increases rapidly.
According to Wikibon, it was predicted that Big Data market would grow 60% each year, 5.1 billion dollar by 2012 and 53.4 billion dollar by 2017. A strategy which helps accurately understand, secure and use Big Data technology is required.
- Current data management by K-Water
-
Allotment of data currently owned by K-Water is estimated to be more than 37,000 GB and 60,000 data on water resources /min. and 370,000 data on waterworks /min. are acquired in real time through automatic measuring equipment on field.
- Examples of data owned by K-Water
- - Water resources : BOD, rainfall, water temperature, turbidity, algae, water level of dam, discharge flow, satellite image, etc.
- - Waterworks : Chlorine concentration, result of water analysis, water pressure, history of incidents around facilities
- - Cities : Sales price, number of population, type of companies moving in, operating rate, etc.
- - Management : Manpower, debt ratio, budget, charges, type and number of civil complaints, etc.
- Direction of the use of Big Data
-
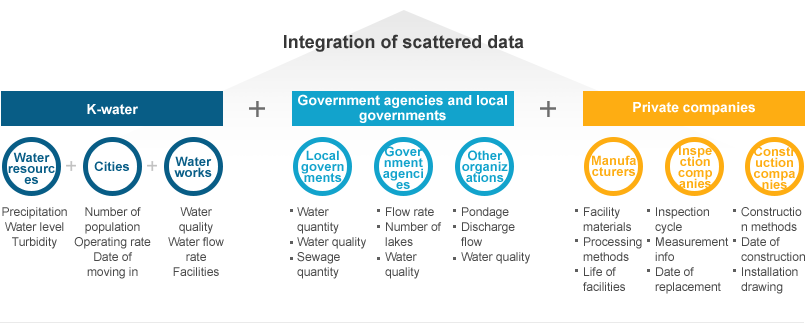
- Integration of scattered information by business and organization
- - Integration of data inside K-water : An organic integration of data which is managed individually by management · technique, water resources · waterworks, local · wide waterworks, and business and is insufficiently connected and linked to each other is required.
- - Integration of data between external relevant organizations : Since information that can be connected with local governments and government agencies are scattered and severed, data between relevant organizations is required to be combined.
- Management of data by K-Water
- If K-Water first develops and starts using a technique of managing Big Data as an organization specialized for water, it can create immense additional value that has never existed before. However, using simple data as smart and premium data with good quality requires more solid preparation.
Having data and tools does not mean that you can create values. We need to cultivate experts in Big Data who can draw significant insight from mass data and deliver such to customers in an easy way or create a whole new service with the use of data.
We also have to prepare countermeasures against related laws in collecting and using data in order to protect the rights of data owner.